ECZEMA FACTS
- Eczema is a condition where parts of the skin become itchy, inflamed, red, and rough.
- Keeping the skin moisturized can prevent certain kinds of eczema.
- It is important to distinguish the different causes of eczema because effective treatments can vary.
- Certain foods could make eczema worse such as dairy, peanuts, wheat, or soy.
- Eczema is not a contagious condition.

WHAT IS ECZEMA?
Eczema is a skin condition that causes the skin to become inflamed, itchy, scaly, red, or irritated.
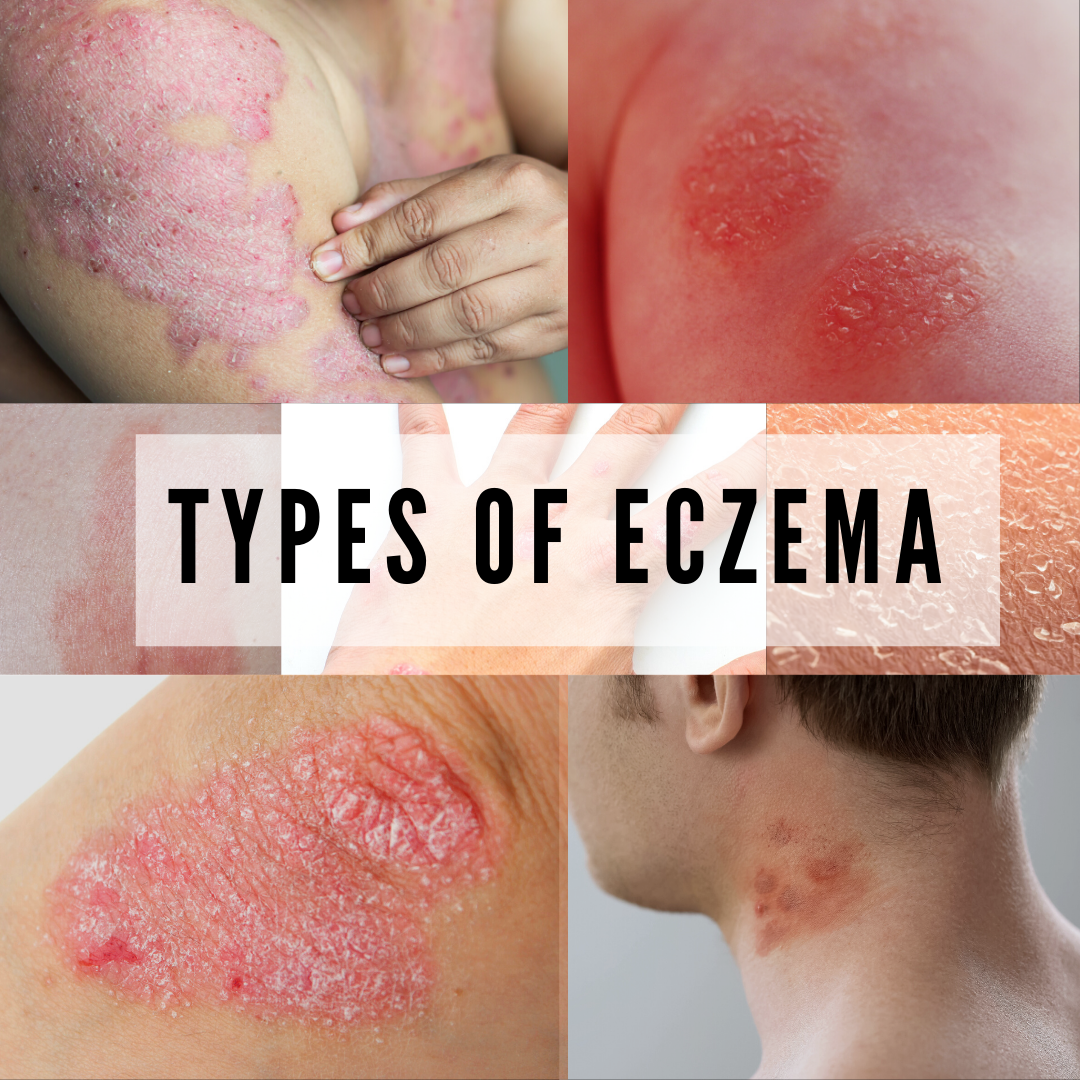
The word "eczema" is also used specifically to refer to atopic dermatitis, the most common type of eczema, however there are 7 known types of eczema.
The appearance of skin affected by eczema will depend on how much a person scratches it, and whether the skin is infected. Scratching and rubbing further causes irritation on the skin, increases inflammation, and can worsen eczema.
All forms of eczema will itch.
Sometimes the itching happens before the rash appears. Eczema rashes most commonly appear on the face, back of the knees, wrists, hands, or feet but it may also affect other areas as well.

TYPES OF ECZEMA AND ITS SYMPTOMS
Atopic dermatitis
The most common form of eczema. It usually starts when someone is young, and often gets milder or goes away by adult age.
"Atopic" refers to a group of diseases including the immune system. Dermatitis means an inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis happens when the skin’s natural barrier against irritants and allergens is weakened, so make sure to keep supporting your skin's natural moisture barrier!
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) symtoms:
- Dry skin
- Itching, which may be severe, especially during the night time
- Red to brownish patches, mostly on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees, and in infants, the face and scalp
Atopic dermatitis most often begins before age 5 and may carry on into adulthood. For some, it flares periodically and clears up for a period of time. Atopic dermatitis could remain in remission for several years.
Contact dermatitis
This is a red, itchy rash caused by direct contact with a substance in which the substance irritates and inflames the skin.
There is another type which is allergic contact dermatitis. After repeated contact with the substance, the body’s immune recognition system becomes activated and you become allergic to that substance.
Dyshidrotic Eczema
This is a type of eczema where clear fluid filled blisters develop on the soles of your feet, sides of the fingers or toes and palms of your hands.
The Blisters normally last for about two to four weeks and could be caused by allergies or stress. The blisters are often very itchy. The skin can also scale, crack, and flake from these blisters.
Hand eczema
An inflammation of the skin of the hands that can be caused by contact allergens such as rubber chemicals, but other external factors such as outside irritants can also cause it.
In hand eczema, your hands get red, itchy, and dry and they may form cracks or blisters.
Neurodermatitis
A skin condition that starts with an itchy patch of skin. It is similar to atopic dermatitis. It causes thick, scaly patches to appear on your skin. Scratching makes it even itchier. Scratching the skin could cause the skin to appear leathery and thickened.
Neurodermatitis usually starts in people who have other types of eczema or psoriasis. Stress could also trigger it.
In neurodermatitis, thick, scaly patches form on your arms, legs, back of your neck, scalp, bottoms of your feet, backs of your hands, or genital. These patches can be very itchy, especially when you’re relaxed or asleep.

Stasis dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis is skin inflammation that develops in people with poor blood circulation. It's common on the lower parts of the legs. When blood collects or pools in the veins of the lower legs, the pressure on the veins increases. Legs can swell up and varicose veins can form.
Nummular eczema
This is a type of eczema that causes coin-shaped spots to form on your skin. Nummular eczema looks very different from other types of eczema, and it can itch a lot. These patches are often itchy and well-defined.
Nummular eczema can be triggered by a reaction to an injury, such as a burn, cut, or scrape, or insect bite. Dry skin can also cause it.These can last for several months and the eczema spots could be 1 or many.
It's best to work with a doctor such as a dermatologist or allergist to help find your eczema causes so you can find the appropriate treatments. Avoiding specific triggers or allergens can help to prevent or minimize flare-ups.
Life with eczema can seem intimidating not knowing how the day after today will treat you, but figuring out the triggers goes a long way in managing flare ups and symtoms!
Eczema Triggers:
Triggers for eczema include environmental exposures and allergens.
Common eczema triggers include
- extended exposure to dry air common in winter. any extreme heat or cold
- dust mites which are a common allergen
- Certain ingredients in common household items may also trigger a reaction such as:
- formaldehyde found in some adhesives like glue or bandages
- cocamidopropyl betaine in shampoos or cleansers.
- Fragrance
- Isothiazolinone in some antibacterial wipes
- Pet hair
- A new clothing detergent
- Certain types of fabric rubbing on the skin like wool or polyester.
Figuring out what is triggering your eczema and avoiding contact with them is ultimately the best way to treat your eczema.
If you can't pinpoint your eczema trigger yourself, ask an allergist or dermatologist about a skin patch test in which they will test for several chemicals found in household products to narrow down what exactly is irritating your skin.
Product For Eczema
The fighter gel has ingredients like organic gotu kola, or centella asiatica which are proven to help with eczema due to the anti-inflammatory and skin barrier supporting properties.
Contains MSM - a type of sulfur that reduces inflammation in skin and improves skin quality to fight eczema. This makes the fighter gel a great eczema product.
It also contains peppermint oil which has evidence that it can provide relief for chronic itching which is great for reducing the itching symptom of eczema.
Other Eczema Treatments:
There are some medications which may be effective for eczema, however note that many medications are for temporary use only and contain side effects.
For all eczema treatments, keep skin hydrated with an eczema safe product like a fragrance free moisturizer that that doesn't contain any of your triggers.
Steroid Creams
Steroid creams may be prescribed for eczema because they reduce inflammation and reduce the skin's immune response in the applied area. These creams may only be used for a week or two at a time depending on strength.
Side effects may be worsened acne or rosacea.
Skin thinning may occur when used together with a tight dressing or bandage.
Other Immunosuppresants
Medications such as predisnone or other immune system supressants may be prescribed, however these can have major side effects. If these are prescribed to you, it is most likely because you have a severe case.
Overall, eczema is a very frustrating condition due to the intense itching sensation and the appearance of the rash may be frustrating for some, but with the above tips, you will surely find a way to avoid your eczema triggers and treat your eczema flare ups if they do happen.
References:
Pharmacological Effects of Centella asiatica on Skin Diseases: Evidence and Possible Mechanisms: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/5462633/
An overview of the different types of eczema: https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/
Effectiveness of topical peppermint oil on symptomatic treatment of chronic pruritus: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5066694/











14 comments
Nikki
I always thought I just had contact dermatitis… but I actually have two types.
Dyshidrotic Eczema. When I was younger, I use to get these little blister bubbles on my fingers. Tiny things that I would pick on and pop. They left tiny holes where the blister was. I still get them every once in awhile.
Neurodermatitis. I have this at my ankle on both feet. Sometimes it itches so bad… and sometimes it’s there, but doesn’t itch. That’s happening right now on my left foot/ankle. And it’s always in the same spot. I have a patch on my right hand too. Same thing. Always on the right hand , on the side of my wrist/palm area.
Lily
I’ve had eczema ever since I was born and I’ve had it all over my body. Especially when it got infected it would ooze and having eczema on my neck and scalp was horrible, especially when it flaked like dandruff and my hair would always look oily when I put cream on. About three years ago I got prescribed dupixent and it has changed my life completely. I do have eczema flare ups here and there but it’s 99% better than what it used to be. Note I’ve also been prescribed plenty of different creams and ointments and even Eucrisa but dupixent was a life changer for me.
Olive
I have nummular eczema all over my body. It’s really itchy and irritating. I’ve had it since I was 8 years old. It goes away and then flares up again. This time round it’s not going away. I still have the brown spots and new ones keep showing up. I’ve used all the creams, ointments, shampoos and soaps prescribed to me but nothing. I would really like to know that to use so I can get rid of them. Also what triggers it so I can prevent the flare ups.
Mary
My face has a scab on my cheek and others are developing in more places. I also have them on my body; the itching is awful
Cody Reed
Raw honey seems to be helping mine. Just cover the area and cover it with a bandage or cloth. Don’t be a tight wad. Use lots of honey. The sugars starve bacteria of oxygen and the skin heals quickly.
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.